Recent Learning Materials

Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Structure, Functions, and Examples
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Definition The apical layer of the stratified cuboidal epithelium is made up of cuboidal cells, but the lower layer can either be
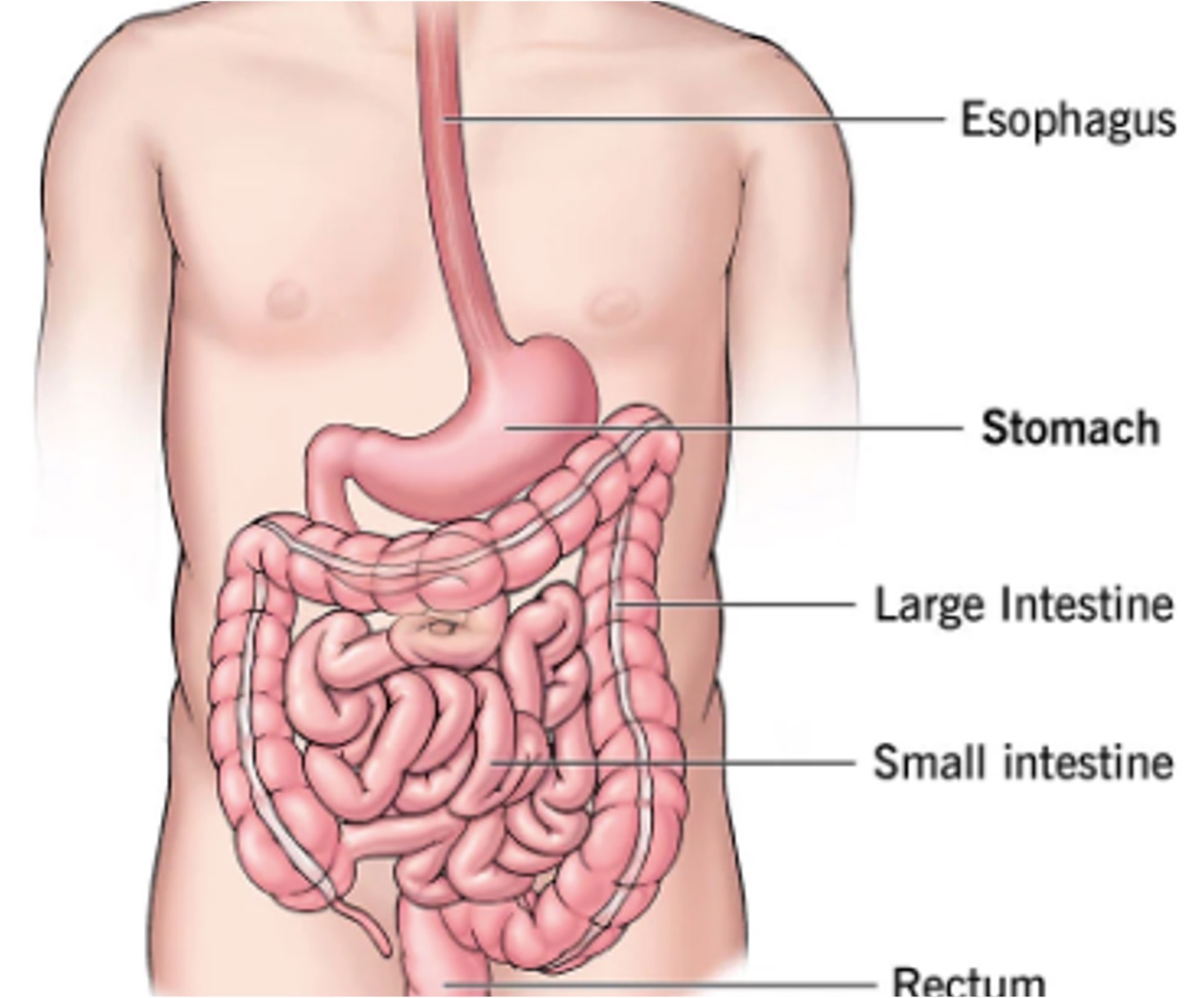
Human Digestive System: Organs, Functions, And Diagram
Human Digestive System Definition The human digestive system is made up of the alimentary canal, several auxiliary organs, and a variety of digestive activities which

Citrate Utilization Test: Principle, Procedure, and Results
What is Citrate Utilization Test? By measuring an organism’s ability to use citrate as its sole form of energy, the IMViC test (Indole, Methyl Red,

MHC Class I Vs MHC Class II: Definition, 15 Differences, Examples
MHC Class I Vs. Class II Differences (MHC I Vs. MHC II) MHC Class I Vs MHC Class II S.N. Characteristics MHC-I Molecule MHC-II Molecule

Protein Synthesis In Eukaryotes: Definition, Enzymes, & Process
Protein Synthesis In Eukaryotes Definition During protein synthesis, the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule is translated into the sequence of amino acids. The mRNA is produced

Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Structure, Functions, & Examples
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Definition The apical layer of stratified cuboidal epithelium consists of cuboidal cells, whereas the bottom layer may be cuboidal or columnar. The

Hydrogen Sulfide Test: Principle, Procedure, Uses, & Interpretation
Hydrogen Sulfide Test Definition The capacity of some microbes to break down molecules containing Sulphur (Sulphur) into hydrogen sulphide (H2S) during metabolism is frequently used
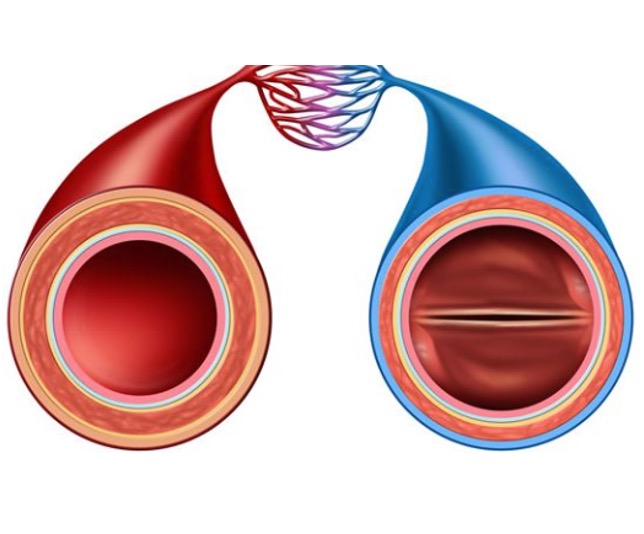
Arteries Vs Veins: Definition And Major Differences
Arteries Vs Veins Overview The two primary types of blood vessels in the body through which blood flows are arteries and veins. The veins return deoxygenated

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)- Definition, Structure, Functions And Diagram
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Definition The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a vast network of membrane-limited channels that is found in the cytoplasm of the majority of

Plasmodesmata- Definition, Structure, Functions And Diagram
Plasmodesmata Definition Each tiny cytoplasmic channel, known as a plasmodesma, that connects a live cell to its next living cell in a higher plant is

Microtubules: Definition, Structure, & Function
Microtubules Definition All eukaryotic cells have microtubules in their cytoplasm, with the uncommon exception of human erythrocytes. They are small, bead-like, hollow tubular structures that

Neutrophils: Definition, Structure, Count, Range, Functions
Neutrophils Definition Neutrophils are a type of white blood cells (leukocytes) that are an important part of the immune system and helps the body fight

Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis: Similarities And Differences
Similarities Between Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Both the Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis processes, which use energy to move particles in and out of the cell, are examples of

Amensalism (Antagonism) Interaction: Definition, Types, & Examples
Amensalism (Antagonism) Definition A negative ecological relationship called Amensalism occurs when one species suffers harm or extinction while the other either gains or is unharmed.

Z-Test- Definition, Formula, Examples, Uses, Z-Test Vs T-Test
Z Test Definition To compare or evaluate the importance of several statistical studies, particularly the mean of a sample from a population having a normally

Voges Proskauer (VP) Test: Principle, Procedure, Results, & Uses
Voges Proskauer (VP) Test Overview Objective of Voges Proskauer (VP) Test Based on the generation of neutral products, to distinguish between two primary kinds of

Types Of Crystals In Urine: Types, Causes, and More
Types Of Crystals In Urine Overview There are several distinct compounds in the urine. These substances have the potential to crystallize into salt under certain conditions.
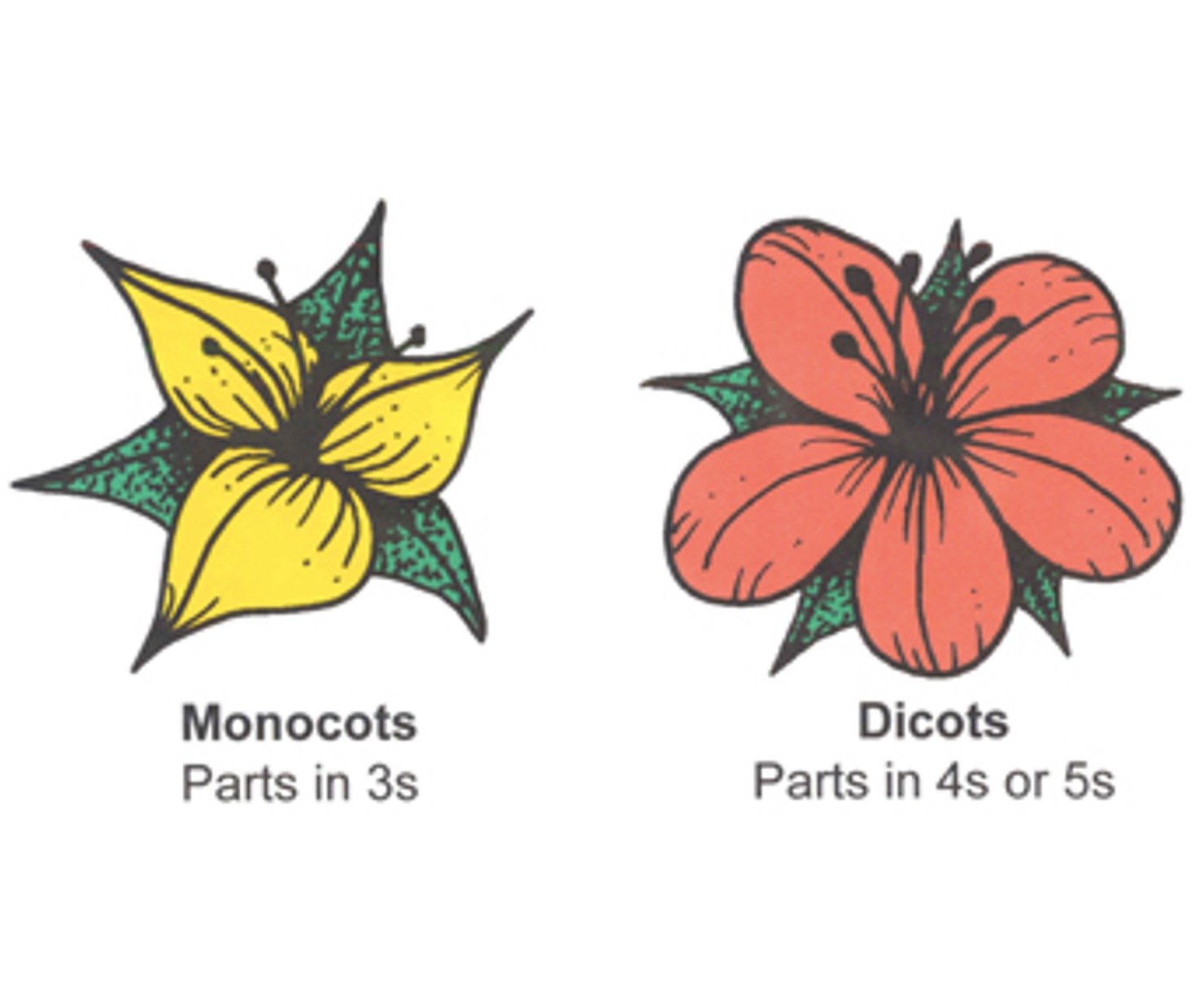
Monocot Vs Dicot Flower: Definition, Structure, Differences, & Examples
Monocot Vs Dicot Flower Overview Definition of Monocot Flower Condensed branch regions called monocot flowers are explicitly designed for the purpose of sexual reproduction. The main

Plant Physiology
Infectious Biology

Human Physiology

Genetics

Cell Biology
