Arteries Vs Veins Overview
The two primary types of blood vessels in the body through which blood flows are arteries and veins. The veins return deoxygenated blood from the tissue capillaries to the heart while the arteries transport oxygenated blood away from the heart.
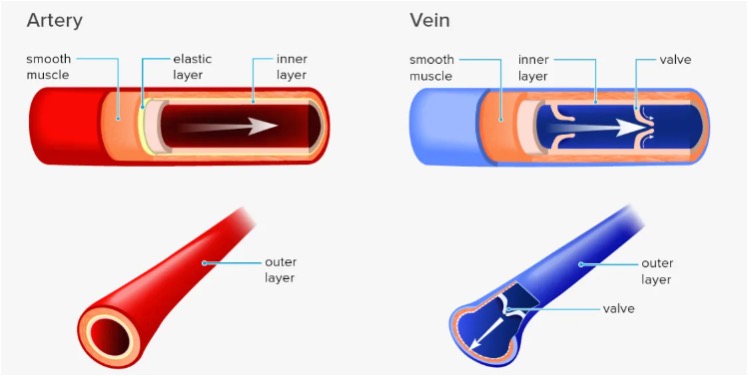
Arteries Vs Veins
| S.N. | Character | Arteries | Veins |
| 1. | Definition | Blood vessels transport blood away from the heart. | Blood vessels transport blood to the heart for oxygenation. |
| 2. | Color | Arteries look red. | Veins look blue (But they only appear blue as blue light is reflected back to our eyes). |
| 3. | Position | Usually positioned deeper within the body. | Usually positioned closer to or beneath the surface of the skin. |
| 4. | Transport/Carry | Oxygenated blood except for the pulmonary artery. | De-oxygenated blood except for pulmonary vein in adult circulation and umbilical vein in fetal circulation. |
| 5. | Oxygen level | Oxygen levels are quite high in arterial blood. | The oxygen level is low comparatively. |
| 6. | Carbon-dioxide level | The CO2 level is low in arterial blood. | The CO2 level is high in venous blood. |
| 7. | Volume of blood | Low (About 15%) | High (About 65%) |
| 8. | Structure | 3 layers of tissue: | Also, possess the same 3 layers but these are much thinner. |
| Outer coat (Tunica adventitia), middle coat (Tunica media) and inner coat (Tunica intima) | |||
| 9. | Tunica adventitia | Less developed. | More developed. |
| 10. | Tunica media | More muscular. | Less muscular. |
| 11. | Tunica intima | Endothelial cells are more elongated. | Endothelial cells are less elongated. |
| 12. | Thickest layer | Tunica media | Tunica adventitia |
| 13. | Walls | Much stronger and rigid than veins. | Less strong or collapsible walls. |
| 14. | Muscularity | More | Less |
| 15. | Flexibility | Highly flexible | Not very flexible |
| 16. | Lumen | Much narrower lumen | Comparatively wide |
| 17. | Blood pressure | Higher in arteries | Lower in veins |
| 18. | Movement of blood | Spurty movement | Sluggish movement |
| 19. | Pulse (wrist) | Detectable (radial artery) | Not detectable. |
| 20. | Valves | Absent (except for semi-lunar valves). | Contain valves to help keep blood flowing in the right direction. |
| 21. | Pathway of blood flow | Very distinct | Sometimes indistinguishable because of many interconnections |
| 22. | Collapsing of vessel | Would generally remain open if blood flow stopped, due to their thick muscular layer. | Would collapse if blood flow stops. |
| 23. | Injury to the Blood Vessel | Squirting blood | Pooling of blood |
| 24. | Contraction of muscle | Present | Absent |
| 25. | At the time of death | Arteries empty up at the time of death. | Veins get filled up at the time of death. |
| 26. | Types | Pulmonary arteries | Deep veins |
| Systemic arteries | Superficial veins | ||
| Pulmonary veins Systemic veins | |||
| 27. | Associated Diseases | Atherosclerosis, Angina Pectoris, Artherogenesis- myocardial ischemia. | Deep vein thrombosis, varicose veins. |
References
- The Difference Between Veins & Arteries
- Difference Between Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries






Pingback: Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Structure, Functions, and Examples