Abdominal Cavity: Definition, Function, and Diagram
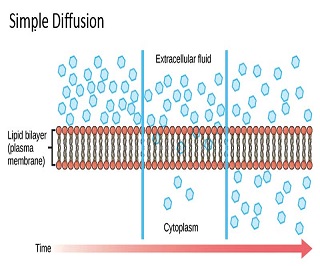
Definition of the Abdominal Cavity The abdominal cavity is a cavity in animals’ torsos that lies between the thoracic and pelvic region divided by the diaphragm. The peritoneum is a protective covering that borders the abdominal cavity and functions in immunity, supporting organs, and fat storage. As illustrated in the figure below, the abdominal cavity …
Abdominal Cavity: Definition, Function, and Diagram Read More »